 |
 |
|
Menu
—
Leather-leaf
—
Sheep laurel
—
Labrador tea
—
Jack pine
|
|
Chamaedaphne calyculata 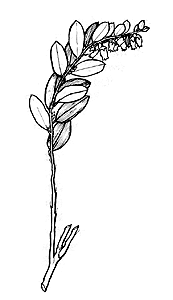 |
Leather-leaf Botanical Information
|
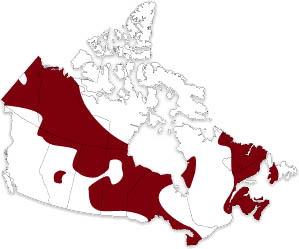 Can be found in
Can be found in
|
Points of Interest
|
|
|
Kalmia angustifolia 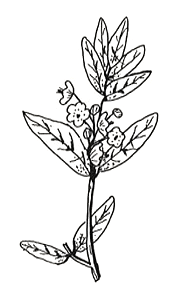 |
Sheep laurel Botanical Information
|
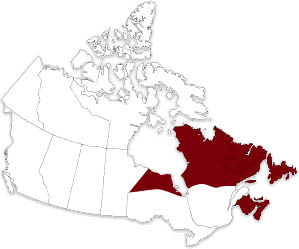 Can be found in
Can be found in
|
Points of Interest
|
|
|
Ledum groenlandicum 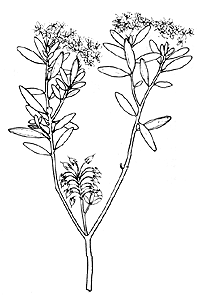 |
Labrador tea Botanical Information
|
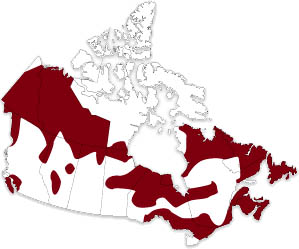 Can be found in
Can be found in
|
Points of Interest
|
|
|
Pinus banksiana 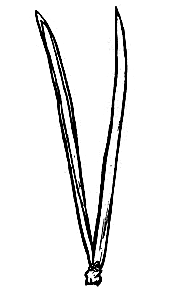 |
Jack pine Botanical Information
|
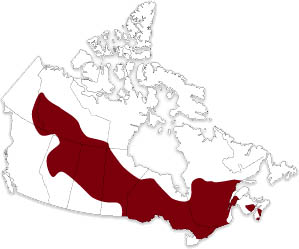 Can be found in
Can be found in
|
Points of Interest
|
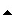
|
|
Rosa acicularis  |
Wild rose Botanical Information
|
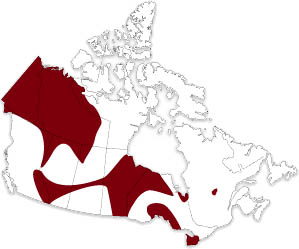 Can be found in
Can be found in
|
Points of Interest
|
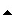
|
|
Sarracenia purpurea  |
Pitcher plant Botanical Information
|
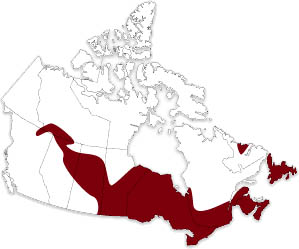 Can be found in
Can be found in
|
Points of Interest
|
|